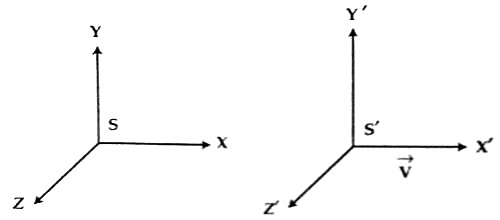
Newtonian Spacetime differs from Relativistic spacetime in that time is considered an absolute (i.e. ). Transformations between reference frames can be achieved with Galilean transformations. A particle traveling along the x axis in at a constant speed u, has a speed found by:
remembering that the first derivative of position is velocity, and the second derivative of motion is acceleration
is derived from of the Galilean transformations.